

Because the z-test is to the left of the critical z-value, we reject the null hypothesis. The critical z-value = –1.645 for this test has probability 0.05 to its left tail, according to the Normal Table (see Appendices). Make a decision: Since α > p-value, reject H 0.Īn alternative approach is to find the z-test corresponding to the sample mean x ¯ = 16. Because a 1.87 percent chance is small, the mean time of 16 seconds or less is unlikely to have happened randomly. Interpretation of the p-value: If H 0 is true, there is a 0.0187 probability (1.87 percent), that Jeffrey's mean time to swim the 25-yard freestyle is 16 seconds or less. The following examples illustrate a left-, right-, and two-tailed test. This makes the data analyst use judgment rather than mindlessly applying rules. Similarly, for a large p-value such as 0.4, as opposed to a p-value of 0.056 (alpha = 0.05 is less than either number), a data analyst should have more confidence that she made the correct decision in not rejecting the null hypothesis. Thinking about the meaning of the p-value: A data analyst should have more confidence that he made the correct decision to reject the null hypothesis with a smaller p-value (for example, 0.001 as opposed to 0.04) even if using the 0.05 level for alpha.H a never has a symbol that contains an equal sign.It is the key to conducting the appropriate test. The alternative hypothesis, H a H a, tells you if the test is left, right, or two-tailed.For this reason, we call the hypothesis test left, right, or two tailed. When you calculate the p-value and draw the picture, the p-value is the area in the left tail, the right tail, or split evenly between the two tails.If no level of significance is given, a common standard to use is α = 0.05.The statistician setting up the hypothesis test selects the value of α to use before collecting the sample data.
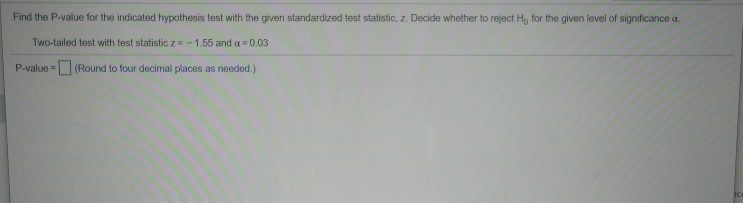
The 1 percent is the preconceived or preset α. In a hypothesis test problem, you may see words such as, the level of significance is 1 percent.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
